Ktirio Urban Building (KUB) User Manual
1. Introduction
Ktirio Urban Building (KUB) is a simulation tool developed under the European project HiDALGO2. It enables detailed urban energy modeling by integrating various data sources and simulation parameters.
2. Prerequisites and Installation
3. Quickstart
This section provides a step-by-step guide to running a basic simulation using the Ktirio Urban Building (KUB) application with the Kernante dataset.
3.1. Fetch Input Data
Download the required Kernante input data from CKAN:
$ wget https://ckan.hidalgo2.eu/dataset/a7f354a6-620f-42dc-bda4-7fc945746e57/resource/d0978965-f708-4ee3-bfac-e1c7c99e232c/download/kernante_input.zipUnzip the archive into your working directory:
$ unzip kernante_input.zip3.3. Download the KUB Container
Pull the latest KUB Apptainer image:
$ apptainer pull -F kub.sif oras://ghcr.io/feelpp/ktirio-urban-building:master-sifThis command fetches the container image from the GitHub Container Registry using the ORAS protocol.
3.4. Configure the Simulation
Edit the configuration file kernante_input/kernante.cfg to adjust simulation parameters such as the simulation time frame or output folder.
Ensure all file paths are correct and accessible from inside the container.
3.5. Run the Simulation
export APPTAINER_HOME=$PWD/kub_outputs/
mpiexec -n 4 --bind-to core \
apptainer exec -B ./kernante_input/:/kernante_input/ \
--env OMP_NUM_THREADS=1 kub.sif \
feelpp_kub_cem \
--config-files /kernante_input/IdealHeaters.cfg /kernante_input/kernante.cfg3.6. Visualize the Results
Use ParaView to open the results file:
$ paraview ./kub_outputs/feelppdb/kernante_output/instances/np_4/lod0/exports/City_Energy_Modeling.caseThis will display the simulation results, including temperature distributions and solar masks.
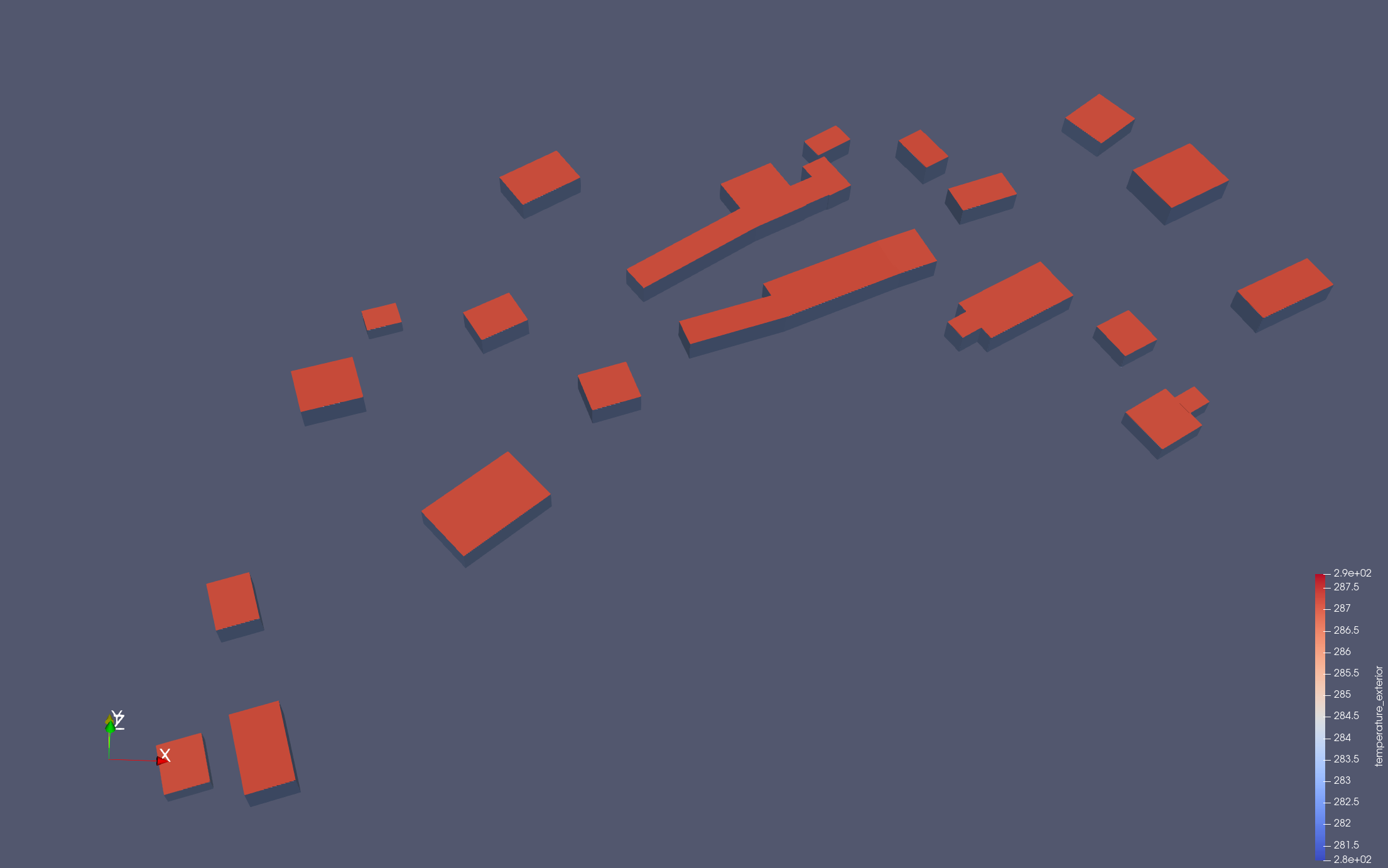
|
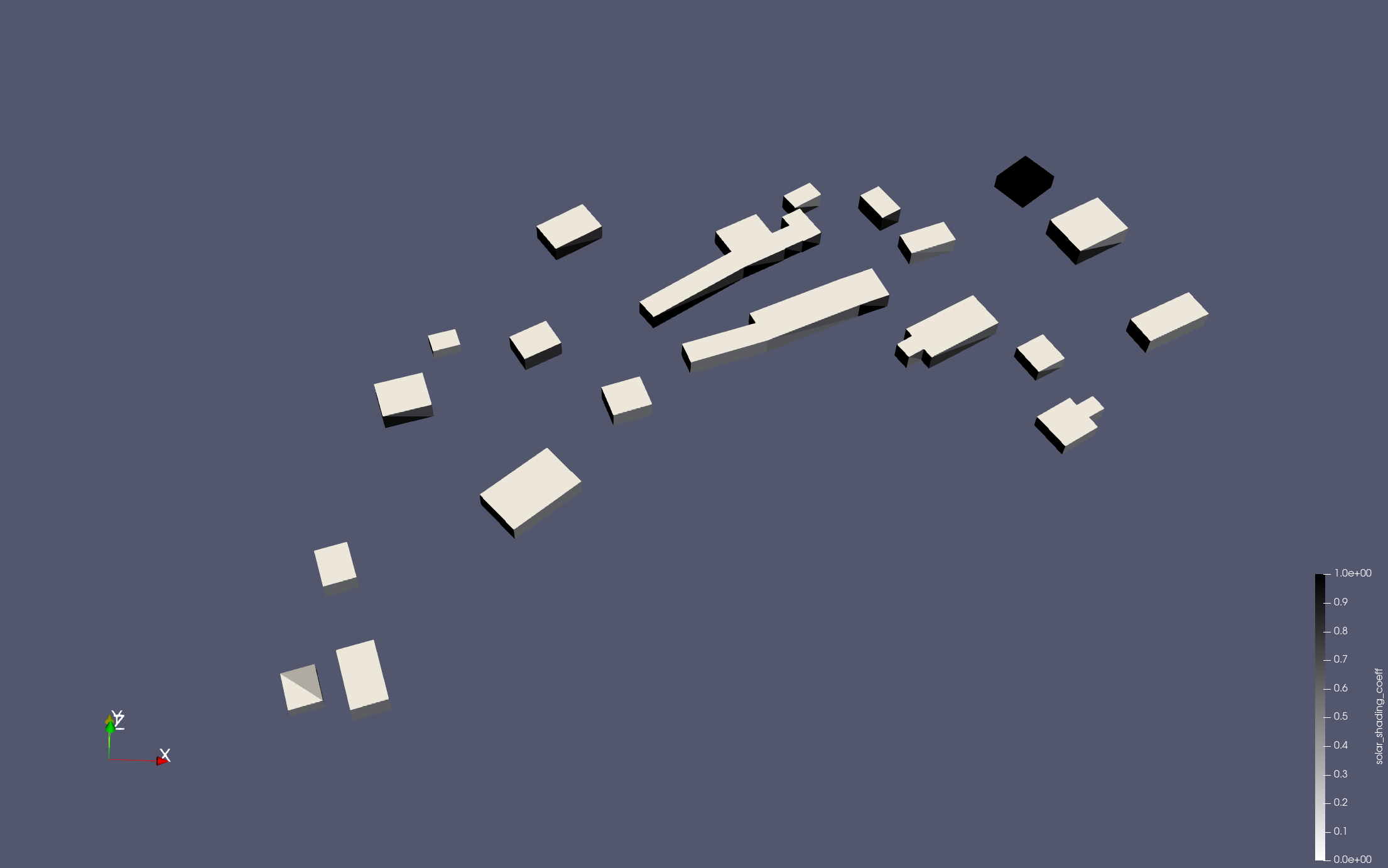
|
3.7. Other Case Studies
Additional case studies and configurations are available at Ktirio Cases.
4. Advanced Usage
4.1. Configuration Options
KUB accepts various configuration options categorized as follows:
4.1.1. Database
-
cem.database.directory: Directory to save all outputs (results, logs, reports, etc.)
4.1.2. Simulator
-
cem.simulator.lod0.modelisation.maxfloors: Maximum number of floors for buildings, assuming each floor is 3m high. -
cem.simulator.lod0.filenames: Path or remote location of the LoD-0 FMU model for simulation. -
cem.simulator.lod0.description.filenames: Path or remote location of the FMU description file. -
cem.simulator.sun.filename: Path or remote location of the FMU model for solar shading coefficients.
4.1.3. Input
-
cem.gis.metadata.filename: Path or remote location of the GIS file associated with the mesh. -
cem.mesh.lod0.filename: Path or remote location of the LoD0 mesh in MSH format. -
cem.weather.filename: Path or remote location of the weather CSV file for the simulation.
4.1.4. Instance
-
cem.instance.time.start: Simulation start time in seconds. -
cem.instance.time.stop: Simulation stop time in seconds. -
cem.instance.time.step: Simulation time step in seconds. -
cem.instance.solar_shading.enabled: Enable or disable solar masks computation. -
cem.instance.idealflows.enabled: Enable or disable ideal heating and cooling flows.
4.1.5. PostProcess
-
postprocess.export.outputs.enabled: Enable or disable output exporting in HDF5 format. -
postprocess.export.visualization.enabled: Enable or disable output exporting in EnsightCase Gold format. -
postprocess.export.outputs.csv.enabled: Enable or disable output exporting in CSV format. -
postprocess.export.report.enabled: Enable or disable city report computation and export. -
postprocess.export.report.building.enabled: Enable or disable report computation on a building level.
5. Troubleshooting
-
Ensure all file paths are correct and accessible.
-
Verify that the Apptainer container is properly pulled and the home directory is set.
-
Check that all required dependencies are installed and correctly configured.
6. Additional Resources
-
Feel++ Remote Data: docs.feelpp.org/user/latest/using/tools/remotedata.html
-
ParaView: www.paraview.org/
 .pdf
.pdf