Ktirio Urban Building (KUB) Overview
1. 1. Context and Motivation
Urban areas are increasingly stressed by climate change, rapid population growth, and aging infrastructure. City planners, architects, and engineers need tools to assess building energy performance, thermal comfort, and environmental impacts at city scale. Traditional building simulation tools often focus on single buildings or small clusters, lacking scalability and integration with heterogeneous urban datasets (GIS layers, weather records, building stock information).
The HiDALGO2 Center of Excellence aims to provide an end-to-end ecosystem for high-resolution, large-scale urban simulations. Within this context, Ktirio Urban Building (KUB) was developed as a lightweight pilot application to:
-
Enable reproducible, city-scale building energy and comfort modeling.
-
Leverage standardized data-management platforms (CKAN, Girder, Zenodo) for input provisioning and output archival.
-
Facilitate deployment on diverse compute infrastructures (EuroHPC supercomputers, private clusters, cloud).
By addressing the gap between isolated building simulators and fully integrated urban workflows, KUB empowers stakeholders to perform climate-resilient design, assess heating/cooling demand, and visualize 3D energy fields across entire metropolitan areas.
2. 2. What Ktirio Urban Building Does
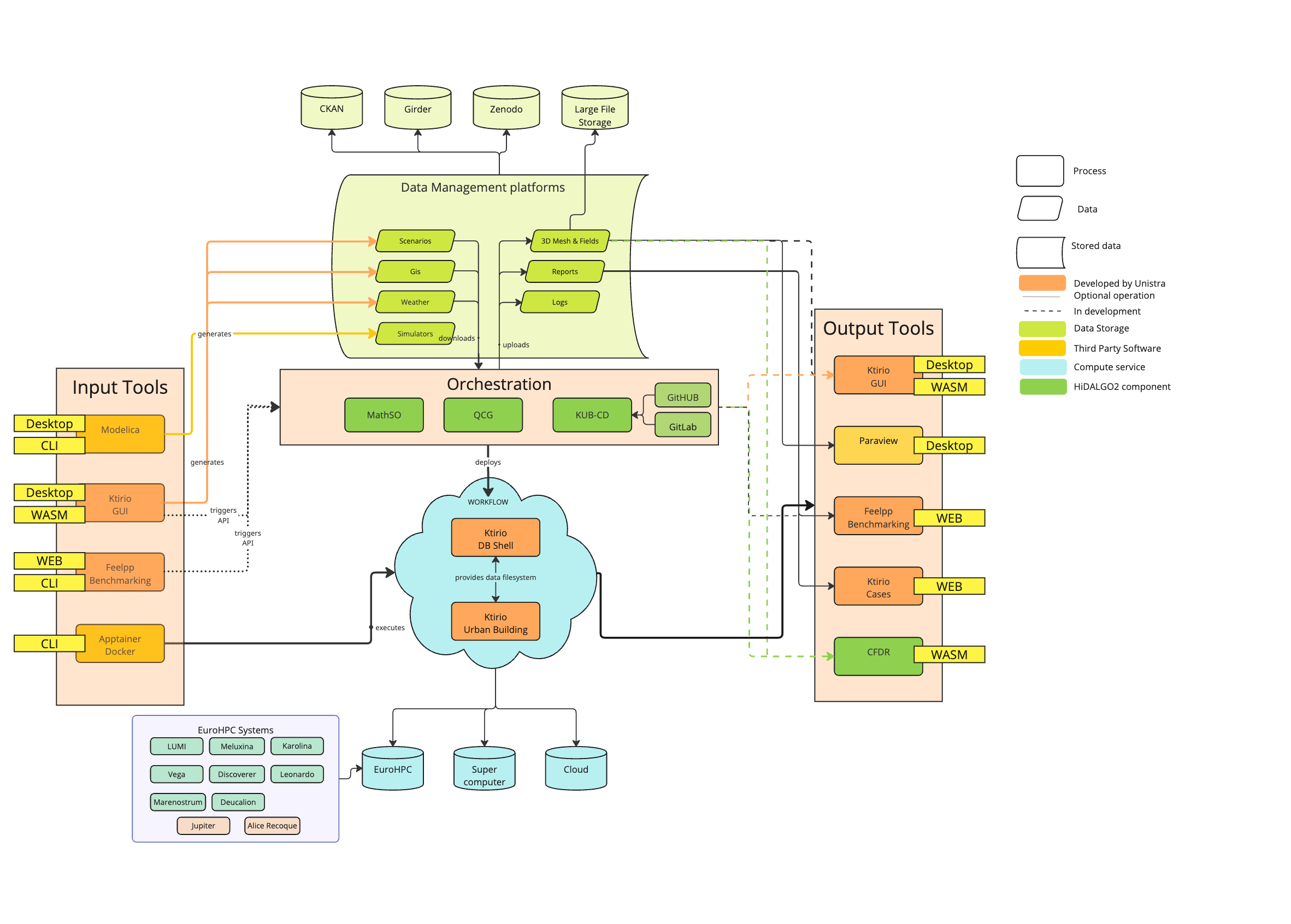
KUB provides a command-line and WebAssembly-enabled interface to orchestrate the following end-to-end process:
-
Data Ingestion
-
Fetches GIS metadata (building footprints, OSM IDs) and LoD-0 meshes describing urban geometry.
-
Imports time-series weather data (temperature, solar radiation, wind, humidity, etc.).
-
Retrieves building-scale FMU models (LoD-0 thermal networks) and associated metadata for output variable definitions.
-
-
Configuration Assembly
-
Merges heterogeneous inputs into a unified configuration framework (
.cfgfiles) that specify simulation parameters (time horizon, time step, max floors, solar shading, ideal flows). -
Supports local paths or Feel++ Remote-Data URIs to automatically download large FMUs and description files at runtime.
-
-
Simulation Execution
-
Launches the Ktirio DB Shell and Urban-Building engine within an Apptainer (or Singularity) container.
-
Distributes computation across multiple MPI ranks, running thermal-physics solvers for each building and computing urban-scale energy exchanges.
-
Optionally leverages EuroHPC systems (LUMI, Karolina, Vega), in-house HPC clusters, or public clouds for parallel performance.
-
-
Post-Processing and Visualization
-
Exports high-resolution 3D meshes, time-series fields (HDF5/CSV), logs, and summary reports.
-
Outputs EnsightCase Gold files for visualization in ParaView or consumption by the Ktirio GUI (desktop/WASM).
-
Computes benchmarking metrics for city-level and (optionally) building-level reports.
-
3. 3. Components
The Ktirio Urban Building workflow is composed of the following key components:
3.1. 3.1 Data Management Layer
-
CKAN, Girder, Zenodo
-
Serve as data repositories for GIS files, mesh files, weather records, FMU packages, and simulation scenarios.
-
Provide remote-data URIs that KUB can use to fetch inputs on demand.
-
-
Feel++ Remote-Data Protocol
-
Standardizes syntax (
girder:{file:<ID>,api_key:<API_KEY>}) for specifying remote resources. -
Ensures reproducibility by versioning datasets and FMU files.
-
3.2. 3.2 Configuration & User Interface
-
KUB CLI
-
Accepts
--config-filesarguments pointing to one or more.cfgfiles. -
Validates required options (e.g.,
cem.gis.metadata.filename,cem.mesh.lod0.filename,cem.weather.filename,cem.simulator.lod0.filenames).
-
-
WebAssembly-Enabled GUI
-
Allows users to construct and preview simulation configurations in a browser.
-
Exports
.cfgfiles compatible with headless KUB executions.
-
3.3. 3.3 Orchestration Services
-
MathSO, QCG, KUB-CD
-
Validate configuration, schedule simulation jobs, and manage dependencies.
-
Interface with CI/CD platforms (GitHub, GitLab) to trigger automated runs on code changes.
-
-
GitHub/GitLab
-
Host source code repositories, enable continuous integration testing (e.g.,
mo2fmuunit tests), and version-control.cfgtemplates.
-
3.4. 3.4 Execution Core
-
Apptainer/Singularity Container
-
Encapsulates the Ktirio DB Shell, Urban-Building solver, and required runtime libraries (Modelica interface, Feel++ libraries, MPI).
-
Ensures reproducible environments across local workstations, HPC clusters, and cloud instances.
-
-
Ktirio DB Shell
-
Manages data I/O between the container’s file system, the local cache (set via
APPTAINER_HOME), and external data repositories.
-
-
Urban-Building Solver
-
Implements the LoD-0 thermal simulation engine, computing heat fluxes, temperatures, solar shading masks, and other building-level quantities.
-
Aggregates results to produce city-scale outputs.
-
3.5. 3.5 Post-Processing & Visualization Tools
-
ParaView
-
Visualizes EnsightCase Gold outputs (3D temperature fields, solar masks).
-
-
Ktirio GUI (desktop & WASM)
-
Provides interactive dashboards for exploring simulation results.
-
Displays time-series plots, histograms, and city maps with energy metrics.
-
-
Reporting Module
-
Generates structured CSV/HDF5 exports for further analysis (e.g., benchmarking, data analytics).
-
Optionally computes expensive building-level reports (enabled via
postprocess.export.report.building.enabled=true).
-
By combining these components, Ktirio Urban Building delivers a flexible, reproducible, and scalable solution for urban-scale building energy and comfort simulations, facilitating climate-resilient planning and data-driven policy making.
 .pdf
.pdf